What is an expression?
An expression is a mathematical sentence written with operators and operands. For example:
3x + y > z
(not A) or B = C
if A then 3 else 4/3 end
8 >> 2
…
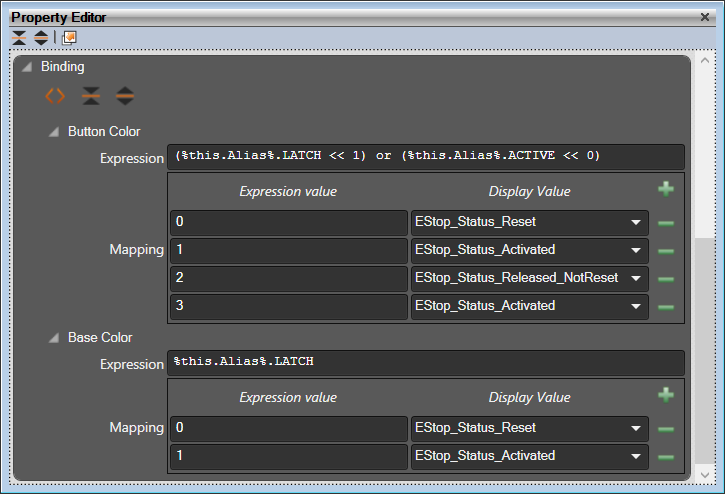
In Sym3 Operator, it is possible to use expressions instead of tags to control objects properties. For every object (2D Component, 3D Component, Window, etc), in the 'Expression' field the user can enter an expression. This screen shows an example of expressions used for the 'Button Color' and 'Base Color' for an EStop.

Avoid the use of a dash ('-') in equipment names and aliases as these are interpreted as the minus operator and will lead to unpredictable results
In Sym3 Operator, the 18 operators are:
+, -, *, /, div, mod, =, <>, <, >, <=, >=, not, and, or, xor, <<, >>.
div refers to Euclidian division
mod is the Modulo (integer remainder after division)
xor is exclusive OR
<< and >> are shifts right and left, operating that way:
5 << 2 = (101 in binary) << 2= (10100 in binary) = 20
20 >> 1= (10100 in binary) >> 1 = (1010 in binary) = 10
The 5 different kinds of variables are:
Boolean, Integer (Short or Long), Double, String.
For each kind of variable, it can be either a constant or a tag.
| Cat. | Operators | Expression | A, B can be | Example | Counter example | Warnings | ||||||
| Bool | Int | Dbl | String | 2 const | 2 tags | 1 tag 1const | ||||||
| 1 | + | A + B | | | | | | | | If StringTag = "abc" StringTag + "def" = "abcdef" | 4 + 5 | * Can’t mix strings with numbers |
| 2 | * ; - | A * B A - B | | | | | | | | If ShortTag = 4 ShortTag - 5 = -1 | 5 - 4 | |
| 3 | / | A / B | | | | | | | | If ShortTag = 4 4 / ShortTag = 1 | "1/1" | * Can't divide by 0 |
| 4 | mod ; div | A mod B A div B | | | | | | | | If ShortTag1 = 4 and ShortTag2 = 13 ShortTag2 mod ShortTag = 1 | 4 mod 2 | * Can’t calculate A mod 0 or A div 0 |
| 5 | < > ; = | A = B A <> B | | | | | | | | If ShortTag = 4 ShortTag + 1 = 5 is True | True = True | * Can’t mix Booleans with numbers * Booleans must be two tags so that Sym3 can calculate |
| 6 | > ; < ; >= ; <= | A < B ... | | | | | | | | If ShortTag = 4 ShortTag > 5 is False | 2 > 1 | |
| 7 | and ; or ; xor | A and B A or B A xor B | | | | | | | | If Tag1 = True and Tag2 = False BoolTag1 Or BoolTag2 = True | True And True | * Booleans must be tags so that Sym3 can calculate |
| 8 | << ; >> | A << B A >> B | | | | | | | | If ShortTag = 4 ShortTag << 1 = 2 | 4 << 1 | * Booleans must be tags so that Sym3 can calculate ; and can be the first operand only * Sym3 reads True=1 and False=0 * Expression can't be calculated with 2 Booleans tags |
| 9 | not | not A | | | | | | | | If ShortTag = 3 Not ShortTag = False | Not False | * Can only be used with tags * 0 means False, every other number means True |
For a 1 Operand-1 Operator expression, Sym3 Operator treats these expressions as the same:
- not A
- (not A)
- not (A)
- not( A)
For a 2 Operands-1 Operator expression, Sym3 Operator treats these expressions as the same:
- A op B
- (A op B)
- (A) op (B)
For an expression containing multiple operators, classic rules of brackets apply. In the absence of brackets the priorities used by Sym3 Operator are:
| Priority levels | Operators |
| 4 | not |
| 3 | * ; / ; div ; mod ; and |
| 2 | + ; - ; or ; xor |
| 1 | << ; >> |
| 0 | = ; <> ; < ; <= ; > ; >= |
| if same level of priority | evaluated from left to right |
Thus, in these expression examples:
| A mod B << C or not E = F | will be evaluated as | ((A mod B)<<(C or (not E)))=F |
| A div B and C | will be evaluated as | (A div B) and C |
Sym3 Operator user can also write an expression containing an "if-then-else" pattern. The classic pattern is:
if <Condition> then <Value1> else <Value2> end
<Condition> is a Boolean tag, <Value1> and <Value2> are variables of any type.
Please note the statement rules:
- the 'else <Value2>' is optional.
- <Value1> or <Value2> can be replaced by ""
- if-then-else patterns can be set as Values inside if-then-else (nested)
- 'end' is mandatory (otherwise an error is reported)
Examples:
| Expression | BooleanTag = True | BooleanTag = False |
| if BooleanTag then 1 else 2 end | 1 | 2 |
| if BooleanTag then 1 end | 1 | |
| if BooleanTag then 1 else end | 1 | |
| if BooleanTag then else 2 end | 2 | |
| if BooleanTag then 1 else 2 | ERROR | ERROR |
| if BooleanTag then 1 | ERROR | ERROR |
| if BooleanTag then (if BooleanTag2 then 1 else 2 end) else (if BooleanTag2 then 3 else 4 end) end | 1 if BooleanTag2 = True 2 otherwise | 3 if BooleanTag2 = True 4 otherwise |